The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is comprised of 10 Southeast Asian countries as well as China, Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand. This new founded pact is seen as an extension of China’s influence in the overall region.
The deal currently excludes the US, which withdrew from a rival APAC trade pact back in 2017. Also, President Trump pulled the American nation out of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TTP) shortly after taking office.
Negotiations over the new RCEP deal started in 2012 and was fully completed and signed this November 2020 on the sidelines of a meeting of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
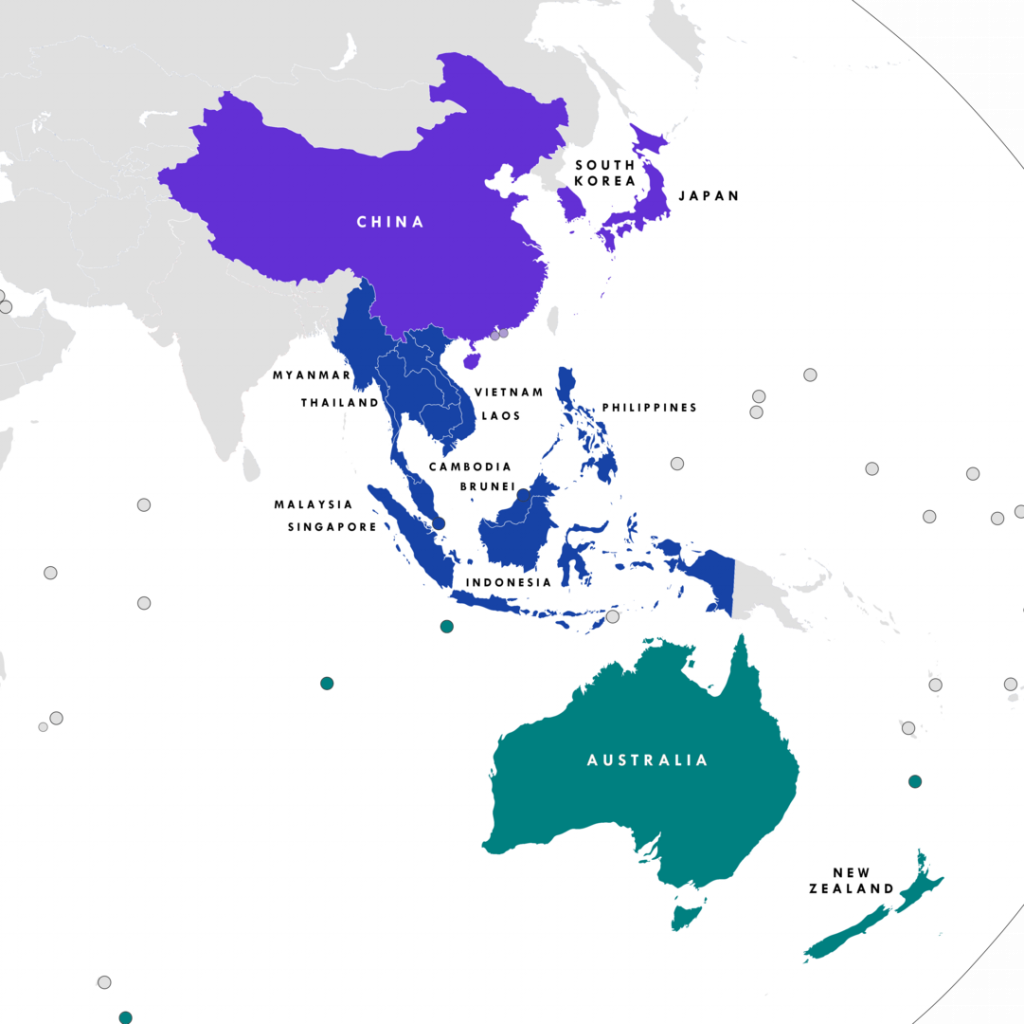
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is comprised of 10 Southeast Asian countries as well as China, Japan, South Korea, Australia and New Zealand. This new founded pact is seen as an extension of China’s influence in the overall region.
The deal currently excludes the US, which withdrew from a rival APAC trade pact back in 2017. Also, President Trump pulled the American nation out of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TTP) shortly after taking office.
Negotiations over the new RCEP deal started in 2012 and was fully completed and signed this November 2020 on the sidelines of a meeting of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
The RCEP isn’t as thorough and extensive, and doesn’t cut tariffs as cohesively as the TPP’s successor, however many analysts believe that the RCEP’s mere size makes it even more significant.
While Mainland China already has numerous bilateral trade agreements, this is the first time it has signed up to a regional multilateral trade pact.
There are a few reasons that member-ing countries want this deal. For starters, world leaders hope that the pact would help spur recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic. The negotiations had been going on for 8 years and for many, shines a ray of light and hope for participating nations. The agreement is seen by many as a victory of multilateralism, and free trade.
Initially, India had also been a part of the negotiations, however pulled out last year over big concerns that lower tariffs could potentially harm local producers. Signatories of the deal claimed that the door remains open for India to join the pact at a future date.
Members of the RCEP man up for nearly one third of the world’s population and account for almost 29% of global gross domestic product.
The newfound RCEP will be larger than both the US-Mexico-Canada agreement and the European Union.
So what will the RCEP do? It’s expected to eliminate tariff on imports within the next 20 years. It also includes provisions on intellectual property, telecommunications, financial & professional services and e-commerce.
The new ‘rules of origin’ which officially define where a product is produced may have the biggest impact. There are already many member states with free trade agreements (FTA) with one another, but there are limitations. The existing FTA can be quite complicated to use compared to RCEP, businesses with global supply chains may face tariffs even within an FTA because their products contain components that are made elsewhere.
For example, a product made in China that contains Australian parts, may face tariffs elsewhere in the ASEAN free trade zone. However, under RCEP, parts from any member nation would be treated equally which may give companies in RCEP participating countries an incentive to look within the trade region for suppliers, therefore boosting the economy.
The RCEP deal could increase global national income by hundreds of billions annually by 2030, and add towards the economy of its member states. Some analysts believe that the deal is likely to benefit China, Japan and South Korea more than other member states as there may be some interesting trade and tariff dynamics to be seen for these countries.
This deal can have a large scale impact towards sourcing and trading: if there are no taxes between the participating nations, it could equal to more business, more businesses looking to produce in China, meaning a substantial growth for our company and yours. DTL Sourcing can be your intermediary, with many years of experience and a large network in China, get in touch today to discuss your business needs.
More information on RCEP official website www.rcepsec.org







